Beetroot, with its vibrant ruby hue, has transcended its humble roots to become a celebrated superfood in 2025. Rich in nutrients, this earthy vegetable is gaining popularity for its remarkable health benefits, particularly for heart health. From reducing blood pressure to boosting stamina, beetroot is a versatile addition to any diet. This blog explores why beetroot deserves a spot in your meals and how it can support your cardiovascular wellness, backed by science and practical tips for everyday use.
Beetroot’s Nutritional Profile

Beetroot is a nutritional powerhouse, offering a range of essential nutrients & antioxidants that promote heart health. A 100g serving of cooked beetroot contains approximately. Beetroot isn’t just a vibrant root vegetable—it’s a cardiovascular powerhouse packed with essential nutrients and natural compounds that support overall wellness.
Here’s what you get in 100g of cooked beetroot:
- Calories: 44 kcal
Low in calories, making it perfect for a heart-healthy, weight-conscious diet. - Fibre: 2.8g
Supports digestion, improves gut health, and helps lower LDL (bad) cholesterol. - Nitrates: 100–150 mg
Naturally converts to nitric oxide in the body, which helps widen blood vessels, improve blood flow, and reduce blood pressure. - Potassium: 325 mg
Regulates heartbeat and counters sodium to help control blood pressure.. - Antioxidants (Betalains):
These give beetroot its deep red hue and offer powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects—protecting your heart, cells, and even your skin. - Vitamin C: ~4–5 mg
Supports immune function, boosts collagen for skin and vessels, and acts as an antioxidant protecting your cells from oxidative stress.
Benefits Beyond the Heart
- Boosts stamina: Nitrates enhance oxygen efficiency, which may improve endurance during workouts.
- Liver detox support: Compounds in beetroot help the liver process toxins.
- Glowing skin: Antioxidants and Vitamin C contribute to healthier, brighter skin.
- Brain health: Improved blood flow may also benefit cognitive function.
A Few Fun Facts about Beetroot!
- Beets were once used as a natural source of lipstick and blush due to their rich pigment.
- Earlier, beet juice was used as a natural ink and paint. Thanks to its rich, deep magenta pigment, it was occasionally used for writing, drawing and even fabric dyeing.
- Beet greens (the leafy tops) are even more nutritious than the root, high in vitamin K, calcium, and iron!
Other Active Compounds
Besides nitrates and betalains, beetroot contains:
- Polyphenols: These plant compounds act as antioxidants and help regulate blood sugar and reduce inflammation.
- Tryptophan: An amino acid that supports mood balance by aiding serotonin production.
- Choline: Aids in liver function, nerve health, and fat metabolism—often overlooked but essential.
- Alpha-lipoic acid (ALA): A potent antioxidant that may help in managing diabetes-related nerve damage and blood glucose control.
How Beetroot Lowers Blood Pressure
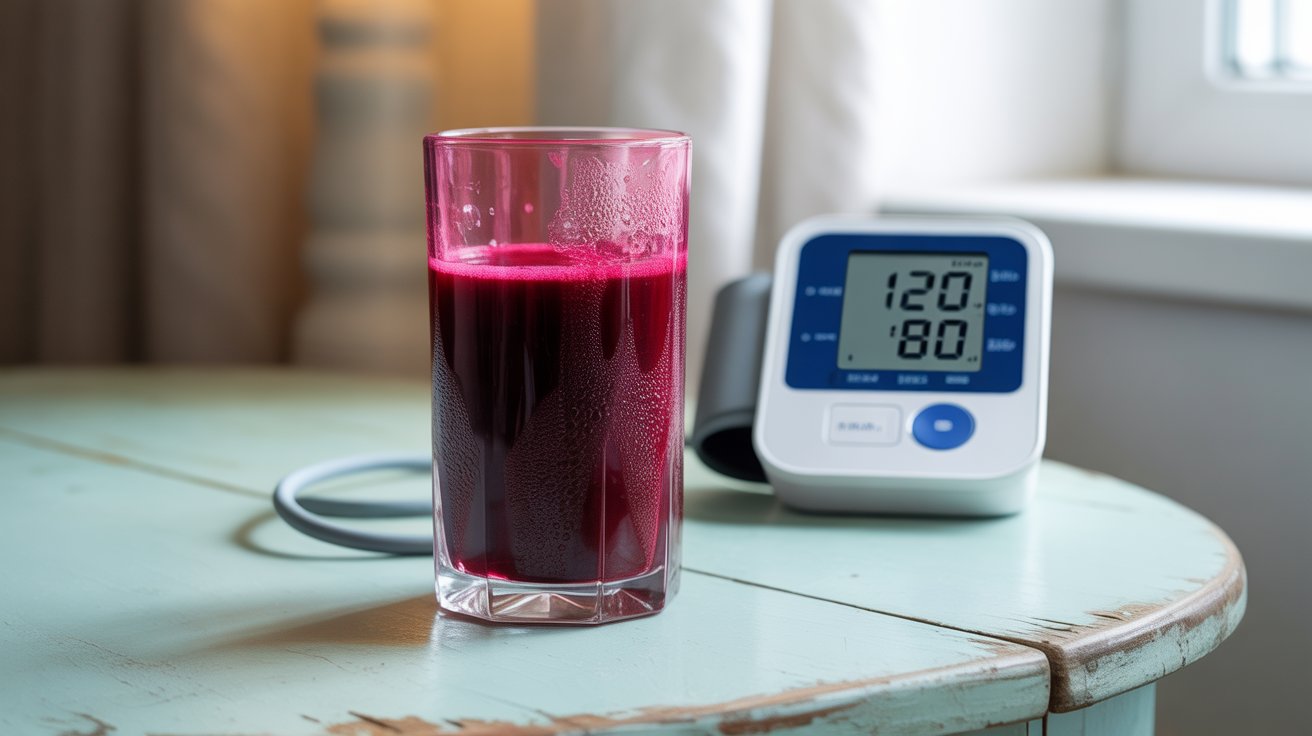
Beetroot’s high nitrate content plays a key role in cardiovascular health.. Nitrates convert to nitric oxide in the body, a molecule that relaxes and widens blood vessels, improving blood flow and reducing blood pressure. Studies, such as one published in Hypertension (2015), show that drinking 250ml of beetroot juice daily can lower systolic blood pressure by 7-8 mmHg, a significant reduction for those at risk of hypertension. This makes beetroot a natural ally for maintaining healthy blood pressure levels.
When you consume beetroot—whether fresh, juiced, or powdered- the nitrates are converted in your body into nitric oxide (NO), a gas molecule that acts as a vasodilator. This means it helps relax and widen blood vessels, allowing blood to flow more freely and reducing the pressure placed on arterial walls. The result? Improved circulation and lower blood pressure.
One of beetroot’s most celebrated health benefits lies in its high nitrate content.
The benefits aren’t just for those with high blood pressure. Athletes, older adults, and individuals dealing with stress-induced blood pressure spikes can also benefit from this nitric oxide boost. The improved vascular flexibility not only supports heart health but also enhances exercise performance, oxygen delivery, and even cognitive function.
If you’re looking for a natural, science-backed way to manage blood pressure, beetroot may be one of the simplest (and most colourful) solutions. Add it to your diet regularly, and your heart will thank you.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Beetroot

Chronic inflammation is a silent contributor to heart disease. Beetroot’s betalains, potent antioxidants, combat inflammation by neutralising free radicals. Research from Nutrients (2017) highlights that betalains reduce markers of inflammation, such as C-reactive protein, which is linked to cardiovascular issues. By incorporating beet into your diet, you can help protect your heart from the damaging effects of long-term inflammation. Chronic inflammation is often called a “silent threat”—you can’t see it or feel it, but it slowly damages your blood vessels and tissues over time. One of the most serious consequences? Heart disease. Prolonged inflammation has been directly linked to atherosclerosis (the buildup of plaque in arteries), high blood pressure, and other cardiovascular conditions. That’s where beetroot steps in as a natural defender.
This ruby-red root is rich in betalains, powerful plant pigments that double as antioxidants and anti-inflammatory agents. These compounds work by neutralising free radicals, unstable molecules that can cause oxidative stress and trigger inflammation throughout the body.
Beetroot and Cholesterol

Beetroot may also support healthy cholesterol levels. Its fibre content binds to LDL (bad cholesterol) in the digestive tract, aiding its excretion. Additionally, studies, like one from the Journal of Nutrition (2018), suggest that beetroot’s antioxidants.
It may increase HDL (good cholesterol) while reducing LDL oxidation, a process linked to artery plaque buildup. Regular consumption of beetroot can contribute to a balanced lipid profile, reducing the risk of heart disease.
Practical Ways to Add Beetroot to Your Diet
Incorporating beetroot into your meals is easier than you think. Here are some simple, delicious ideas:
- Beetroot Juice: Blend fresh beets with a splash of lemon for a refreshing drink. Aim for 200-250ml daily.
- Roasted Beets: Toss cubed beets with olive oil, salt, and ajwain, then roast at 200°C for 30 minutes.
- Salads: Grate raw beetroot into salads with greens, walnuts, and feta for a nutrient-packed meal.
- Smoothies: Combine beetroot with berries, spinach, and yogurt for a heart-healthy smoothie.
- Soups: Whip up a vibrant beetroot soup loaded with desi veggies and topped with spiced curd for a comforting, Indian-style twist.
Beetroot Supplements: Are They Effective?

Beetroot supplements, such as powders or capsules, are marketed as convenient alternatives to fresh beets. While they retain some nitrate and antioxidant benefits, fresh beetroot offers a broader nutrient profile, including fibre, which supplements often lack.
A 2020 study in Food Chemistry found that whole beetroot consumption delivers more comprehensive cardiovascular benefits compared to isolated supplements. If you choose supplements, ensure they’re from reputable brands and complement them with whole foods for optimal results.
Who Should Be Cautious with Beetroot?
While beetroot is safe for most, some groups should exercise caution:
- Kidney Stone Risk: Beetroot contains oxalates, which may contribute to the formation of kidney stones in susceptible individuals.
- Low Blood Pressure: Those with hypotension should monitor intake, as beetroot’s nitrates can further lower blood pressure.
- Allergies: Rare allergic reactions to beetroot may occur; consult a doctor if symptoms arise.
Always consult a healthcare professional before making significant dietary changes, especially if you have underlying medical conditions.
Conclusion
Beetroot’s vibrant colour is matched only by its impressive heart health benefits. From lowering blood pressure to fighting inflammation and supporting cholesterol balance, this superfood is a must-have for a heart-healthy lifestyle. Whether you sip it as juice, toss it in salads, or blend it into smoothies, beetroot is a versatile and delicious way to nourish your body. Make beetroot a regular part of your meals and experience the difference it can make to your heart and overall wellbeing.
Swap one sugary drink for a glass of beetroot juice this week and feel the difference it makes for your heart health.
Beetroot’s vibrant colour is matched only by its impressive heart health benefits. From lowering blood pressure to fighting inflammation and supporting cholesterol balance, this superfood is a must-have for a heart-healthy lifestyle. Whether you sip it as juice, toss it in salads, or blend it into smoothies, beetroot is a versatile and delicious way to nourish your body.
Here’s what just 1 cup a day can do:
- Blood Pressure: Naturally lowers BP by relaxing blood vessels through its rich nitrate content.
- Cholesterol: Helps manage LDL and boost HDL with its fibre and antioxidant profile.
- Inflammation: Betalains work as powerful anti-inflammatory agents to protect heart tissue.
- Stamina: Boosts oxygen efficiency and endurance, making it ideal for active lifestyles.
If you’re someone who enjoys exploring smarter ways to eat, train, and live better, the Alpha Coach die-coaching app has been designed to make that journey smoother. You don’t have to figure it all out alone. Explore more here.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Is Makhana the New Superfood Snack
- Top 7 Healthy Carbohydrate-Rich Foods
- Intermittent Fasting 101: The 16/8 Rule
- What is Quinoa: Health Benefits and Nutritional Values













Leave a Reply